Building a Weather Forecasting Application with Flyte, Pandera, and Streamlit
An End-to-end Online Machine Learning Application
Building a Weather Forecasting Application with Flyte, Pandera, and Streamlit
This is the first in a series of flyte.org projects that demonstrate an end-to-end application using Flyte as one of the components. All of the source code for this project is available in the flyteorg/flytelab repo.
The MLOps ecosystem is maturing at a rapid pace. It's now at the point where data scientists and machine learning engineers have the tools they need to ship model-driven products that would have otherwise required considerable dev ops and frontend engineering effort. In particular, online machine learning is an area that's particularly challenging from an MLOps perspective, and in this blog we'll dive into the process of building robust, reliable, and interactive applications with Flyte, Pandera, and Streamlit.
Motivation
It's a well-established fact in the data science (DS) and machine learning (ML) communities that only a small component of an ML system involves the model-training code: there are a lot of other components that makes it robust, reliable, and maintainable in production.
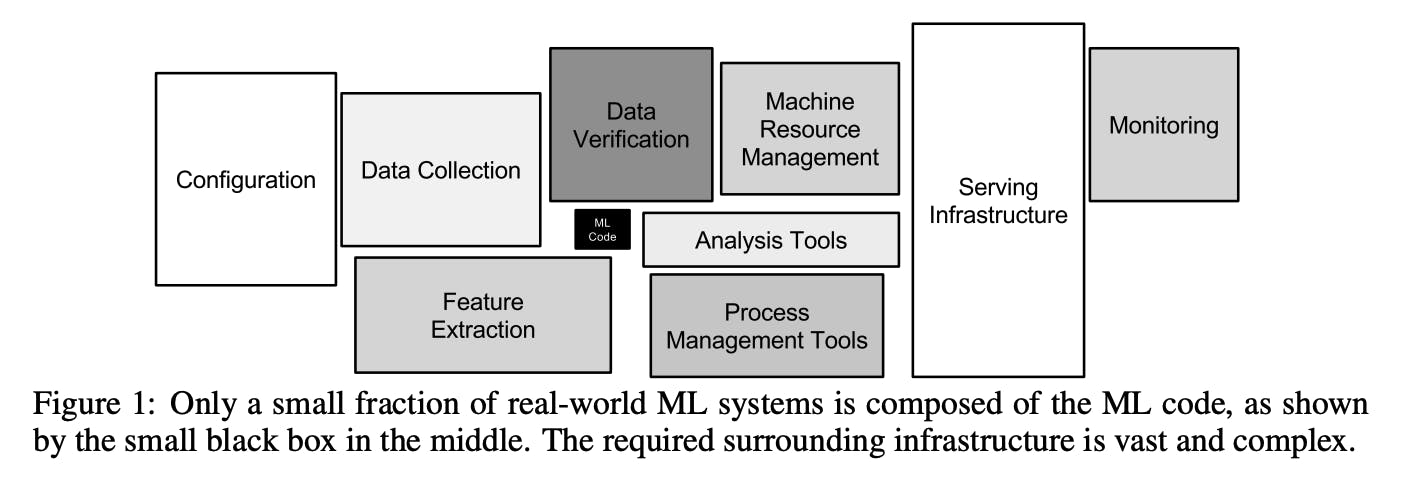
source: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2015/file/86df7dcfd896fcaf2674f757a2463eba-Paper.pdf
In practice, the feedback loop between R&D and production can be long and arduous: DS/ML practitioners formulate appropriate applications (i.e. "should we build this in the first place?"), prototype, and validate models in the lab, and at least in theory, go through a more stringent holistic evaluation of whether a model should be released into the wild. Only if the answer is "yes" might they deploy these models into production where end-users consume the model's outputs.
This whole process is mediated by social forces within the broader organization, including how much trust the people within it have in these kinds of ML systems, including their builders and also internal stakeholders who have an interest in the organization's longterm success. Part of this trust-building process is the degree to which a data team can demonstrate the value, risks, and limitations of ML models before committing to a production deployment. This is why, as part of this case study, we set out to address the following question:
How far can a (potentially small) data team get building and shipping production-grade model-driven data products?
To begin answering this question, we set ourselves the challenge of building an online learning system that updates a model daily and displays hourly forecasts on a web UI.
Why? Because it forces the practitioner to think about:
- Incremental data acquisition and validation
- Model updates in production as a first class citizen
- Evaluation metrics in the deployment setting
It's tempting to treat these three facets of production ML systems as after thoughts in the offline learning setting. However, by going through the exercise of implementing an online learning ML system, we can extract useful design patterns that we could apply back to an offline learning setting.
Offline vs Online Learning
Offline Learning is a setting where a model learns from a static dataset and needs to be updated at some pre-determined cadence, while online learning is setting where a model learns from examples that present themselves to the model only once, in some temporal fashion.
In principal, you might want to consider online learning when:
- Your data isn't static, e.g. data is generated as a function of time
- Your data might be too large to practically store/train a model on all at once
- You can't assume I.I.D. data, e.g. today's data depends on yesterdays, etc.
- Your model needs to be as up-to-date as possible due to the dynamic nature of the underlying phenomenon that produces the data.
Use Case: Weather Forecasting
For this case study we picked hourly temperature forecasting as an appropriate application for building an online learning model, as it fulfills many of the criteria outlined above.
Our objective is to train a model on data managed by NOAA.gov, which offers a web API service for fetching weather data from the global hourly integrated surface database (ISD). This database contains weather-related data from around the world at approximately an hourly resolution:
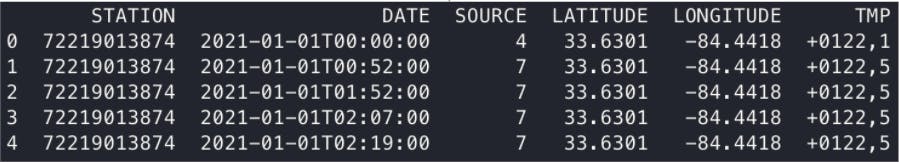
As you can see from the raw sample above, the TMP column contains the temperature data that we're interested in, and we'll need to parse it in order to extract hourly temperatures in degrees Celsius.
The trained model should produce hourly temperature forecasts and update itself daily, which is roughly how often the ISD is updated. For the purpose of the case study, we'll use an autoregressive model, which is one of the simplest models one can use for time series data.
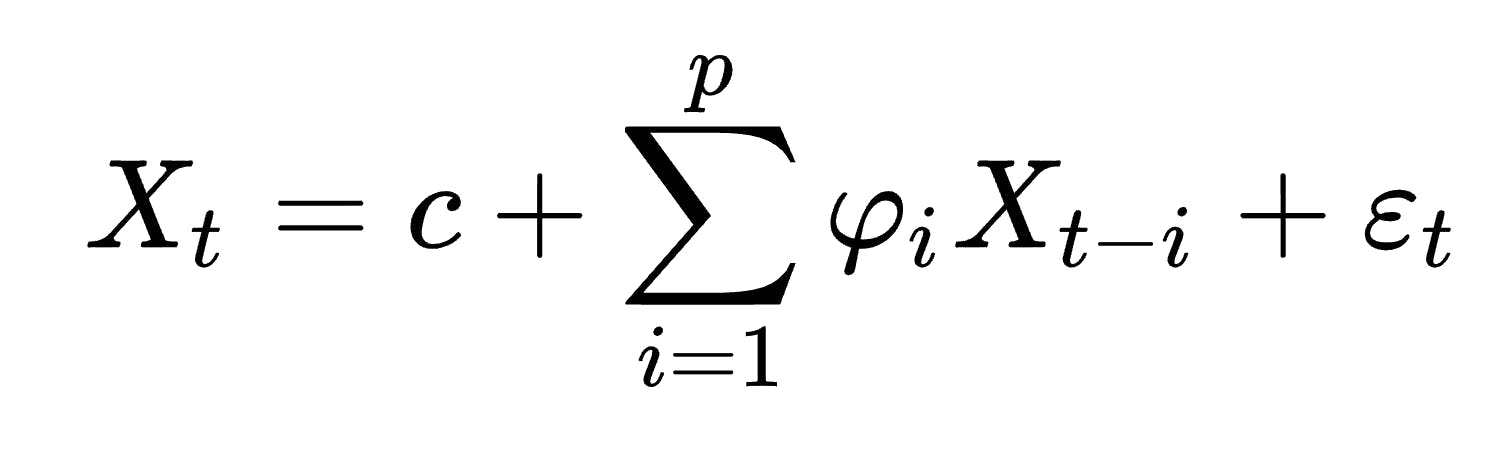
source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoregressive_model
Again, the model-training component of this ML system can always be swapped out for something fancier: the main purpose of this case study is to demonstrate how to put together the various pieces required to build a reliable online learning system.
Finally, as an evaluation metric, we'll implement an exponentially-weighted mean of the absolute error when comparing the ground truth temperature to the model's prediction. Roughly speaking, this would look like:
eps = 0.1
ewmae = 0
for X, y in training_data:
y_pred = model(X)
ewmae = eps * abs(y - y_pred) + (1 - eps) * ewmae
Pipeline Architecture
Now that we have a good handle on the problem set and high-level specifications of the model, we can dig into some of the details of the ML system more broadly. The purpose of this project is to use Flyte, Pandera, and Streamlit to deliver weather forecasts to the end user. Specifically, each library will serve a specific purpose:
- Flyte: task orchestration and execution of the data processing and model-training workload in the cloud.
- Pandera: validation of dataframes as they pass through the pipeline.
- Streamlit: building and deploying a simple interactive UI that displays forecasts.
At a high level, this is the architecture of the application:
Requirements
The main requirements we focused on in this project are to:
- Support incremental model updates with optional pre-training
- Implement evaluation metrics in an online fashion
- Validate raw and clean data from the NOAA API
- Display the latest hourly forecasts in an interactive UI
In the next three sections we'll dive deeper into how each of these tools address these requirements.
Requirement 1: Incremental Model Updates with Recursive, Dynamic Workflows
Flyte is a powerful orchestration platform that enables you to write data processing logic locally and scale it to the resource requirements that you need to go to production. The primary unit of work in Flyte is the task, which can be composed together into workflows.
@task
def process_data(data: pd.Dataframe) -> pd.DataFrame:
...
@task
def train_model(data: pd.DataFrame) -> Model:
...
@task
def generate_predictions(model: Model, new_data: pd.DataFrame) -> Predictions:
...
@workflow
def pipeline(data: pd.DataFrame, new_data: pd.DataFrame) -> Predictions:
model = train_model(data=process_data(data=data))
return generate_predictions(model=model, new_data=new_data)
However, this isn't the only thing Flyte is capable of. Because it supports dynamism in addition to simply constructing a static computation graph, we can perform recursion, which is a key piece that was needed to realize requirement #1: to support incremental model updates with optional pre-training.
The @dynamic function decorator, along with Flyte's native caching functionality, enables us to create a workflow that calls itself, which unlocks a pretty neat construct: the ability to efficiently obtain the model from the previous timestep in order to update the model for the current timestep.
@dynamic(cache=True)
def get_latest_model(
target_datetime: datetime,
genesis_datetime: datetime,
n_days_pretraining: int,
) -> ModelUpdate:
if target_datetime <= genesis_datetime:
# implement optional pre-training here
return init_model(n_days_pretraining=n_days_pretraining)
else:
previous_datetime = get_previous_target_datetime(target_datetime=target_datetime)
# recursion here 🤯
previous_model = get_latest_model(
target_datetime=previous_datetime,
genesis_datetime=genesis_datetime,
n_days_pretraining=n_days_pretraining,
)
return update_model(model=previous_model, ...)
Basically we're defining a dynamic workflow called get_latest_model which takes two parameters:
target_datetime: the current time-step for which to get data and update the model.genesis_datetime: a datetime<= target_datetimethat indicates when the model was instantiated.n_days_pretraining: the number of days looking back fromgenesis_datetimewith which to pre-train the initial model.
Within the get_latest_model function body, we first check if the target_datetime is less than or equal to genesis_datetime. If so, we call init_model, which itself is a Flyte task that contains the logic for initializing the model with some amount of pre-training. This execution path of the workflow is executed pretty much only the first time the pipeline runs.
If the target_datetime is a value some point after genesis_datetime, then what we do is first get the previous_datetime, which would be genesis_datetime when the pipeline runs for the second time. We then invoke get_latest_model with the previous_datetime to obtain the previous_model, and since this dynamic workflow itself is a cached workflow, we immediately get the initialized model from the previous time-step without having to re-initialize it.
Because we're caching the results of get_latest_model, when we move forward in time this recursive dynamic workflow will only have to look back one time-step to fetch the most up-to-date version of the model, then update it for the current target_datetime.
Pretty powerful 🦾 !!!
Requirement 2: Online Evaluation with Strong Types
Because we're updating the model in an incremental fashion with potentially a single training instance on a given update, we also want to evaluate the training and validation performance of our model in an incremental fashion. Since Flyte is a strongly-typed orchestration language, we can explicitly encode all the required states needed for a model:
from typing import NamedTuple
from dataclasses import dataclass
from dataclasses_json import dataclass_json
from flytekit.types.file import JoblibSerializedFile
@dataclass_json
@dataclass
class Scores:
# keep track of mean absolute error
train_exp_mae: float = 0.0
valid_exp_mae: float = 0.0
@dataclass_json
@dataclass
class TrainingInstance:
# definition of the contents of a single training instance
target_datetime: datetime
features: ...
target: ...
ModelUpdate = NamedTuple(
"ModelUpdate",
model_file=JoblibSerializedFile,
scores=Scores,
training_instance=TrainingInstance,
)
In this code snippet we're using a a Flyte type called JoblibSerializedFile to represent a pointer to the model artifact, in this case an sklearn model, along with dataclass and dataclass_json to encode the type for evaluation Scores and TrainingInstances.
We can then define a Flyte task that performs a single model update, computing the exponentially-weighted validation metric before the update using partial_fit, and then computing the training metric after:
from sklearn.exceptions import NotFittedError
def exp_weighted_mae(mae, exp_mae, epsilon=0.1):
"""Exponentially-weighted mean absolute error."""
return epsilon * mae + (1 - epsilon) * exp_mae
@task
def update_model(
model: JoblibSerializedFile,
scores: Scores,
training_instance: TrainingInstance,
) -> ModelUpdate:
features = training_instance.features
target = training_instance.target
try:
y_pred = model.predict(features)
except NotFittedError:
# fallback for when the model hasn't been fit yet, i.e. at initialization,
# using the mean of air temperature features in the past time steps
# to predict the target air temperature.
y_pred = np.mean(features.air_temp_features)
# compute running validation mean absolute error before updating the model
valid_exp_mae = exp_weighted_mae(
abs(y_pred - target.air_temp), scores.valid_exp_mae
)
# update the model
model.partial_fit(features, target)
# compute running training mean absolute error after the update
train_exp_mae = exp_weighted_mae(
abs(model.predict(features) - target.air_temp),
scores.train_exp_mae
)
return model, Scores(train_exp_mae, valid_exp_mae), training_instance
With the ModelUpdate type, we can be confident that, for each update, we have the model artifact along with the metrics and training instance associated with it. What's even better is that we're also guaranteed that the data types have been validated with Flyte's internal type system.
Requirement 3: Data Validation with Pandera
Speaking of validation, validating dataframes (e.g. pandas.DataFrame s) can be a challenge since they are mutable and dynamic data structures with no guaranteed types or properties. Flyte offers the FlyteSchema type, which works with a bunch of different tabular formats like parquet, pyarrow, spark, and pandas. However, if you want to validate the contents of a dataframe beyond the types of each column, Flyte also integrates well with Pandera, which is a statistical typing and data testing tool for validating the properties of a dataframe's contents at runtime.
To use pandera with flytekit, we need to install the plugin with:
pip install flytekitplugins-pandera
Then we can define the pandera schemas that we need to ensure that the data passing through our workflow is what we expect:
import pandera as pa
class GlobalHourlyDataRaw(pa.SchemaModel):
DATE: Series[pa.typing.DateTime]
TMP: Series[str] # raw temperature field
class Config:
coerce = True
class GlobalHourlyData(pa.SchemaModel):
# validate the min and max temperature range in degrees Celsius
air_temp: Series[float] = pa.Field(ge=-273.15, le=459.67)
dew_temp: Series[float] = pa.Field(ge=-273.15, le=459.67)
# pandera supports validating pandas.Index
date: Index[pa.typing.DateTime] = pa.Field(unique=True)
class Config:
coerce = True
As you can see, we've defined two schemas: one for the raw data coming in from NOAA API called GlobalHourlyDataRaw, and another one called GlobalHourlyData for the expected type of the dataframe once we've cleaned it and is model-ready.
We can then define helper functions that are called by a Flyte task to fetch and clean the data:
import flytekitplugins.pandera
from pandera.typing import DataFrame
@pa.check_types
def get_raw_data(...) -> DataFrame[GlobalHourlyDataRaw]:
...
def process_raw_training_data(
raw_data: DataFrame[GlobalHourlyDataRaw]
) -> DataFrame[GlobalHourlyData]:
...
@task(cache=True)
def get_weather_data(...) -> DataFrame[GlobalHourlyData]:
return process_raw_training_data(get_raw_data(...))
Functions decorated with @task automatically check the validity of inputs and outputs annotated with the pandera DataFrame[Schema] type, and for plain Python functions, @p a.check_types makes sure that dataframes types are valid.
You can continue to iterate and refine the schemas over time, and with that you can be more confident that the dataframes in your workflow are property type-checked 🐼 ✅ !
Requirement 4: Display the latest hourly forecasts in an interactive UI
Last but not least, we need a way of displaying our model's forecasts to end users, and for this we'll use Streamlit. To connect Flyte and Streamlit together, all we need to to is use the FlyteRemote client to give us access to the remote execution outputs (i.e. the forecasts), which we can then format and display in the Streamlit script in exactly the way we need.
import pandera as pa
import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
from flytekit.remote import FlyteRemote
from app.workflows import Forecast
remote = FlyteRemote()
st.title("Flytelab: Weather Forecasts ⛈☀️☔️")
class ForecastSchema(pa.SchemaModel):
air_temp: pa.typing.Series[float]
dew_temp: pa.typing.Series[float]
index: pa.typing.Index[pa.typing.DateTime]
@pa.check_types
def get_forecasts() -> pa.typing.DataFrame[ForecastSchema]:
[latest_execution, *_], _ = remote.client.list_executions_paginated(...)
execution = remote.fetch_workflow_execution(name=latest_execution.id.name)
remote.sync(execution, sync_nodes=False)
forecast = execution.outputs["forecast"]
return create_forecast_dataframe(execution.outputs["forecast"])
st.line_chart(get_forecasts())
You can check out the live demo of the app ✨ here ✨.
Takeaways
To summarize all the components that we've used to realize this online learning weather forecasting app:
So returning to the question we posed earlier:
How far can a (potentially small) data team get building and shipping production-grade model-driven data products?
Hopefully this post convinces you that we can go almost all the way! What's missing from this application is model monitoring, assessing dataset shift, and app authentication, and these might be subjects for another post.
What these three tools give us is the power to create robust and reliable model-driven applications with interactive UIs. If this sounds like something you'll need, give Flyte, Pandera, and Streamlit a try and a GitHub ⭐️, and let us know what you think in the comments below!

